2.3.6.2.1. Read analog voltage on a slow analog input
2.3.6.2.1.1. Description
This example shows how to measure the analog voltage of slow analog inputs on the Red Pitaya extension connector. The analog inputs on the Red Pitaya are rated from 0 to 3.3 Volts.
2.3.6.2.1.2. Required hardware
Red Pitaya device
R1 10k potentiometer
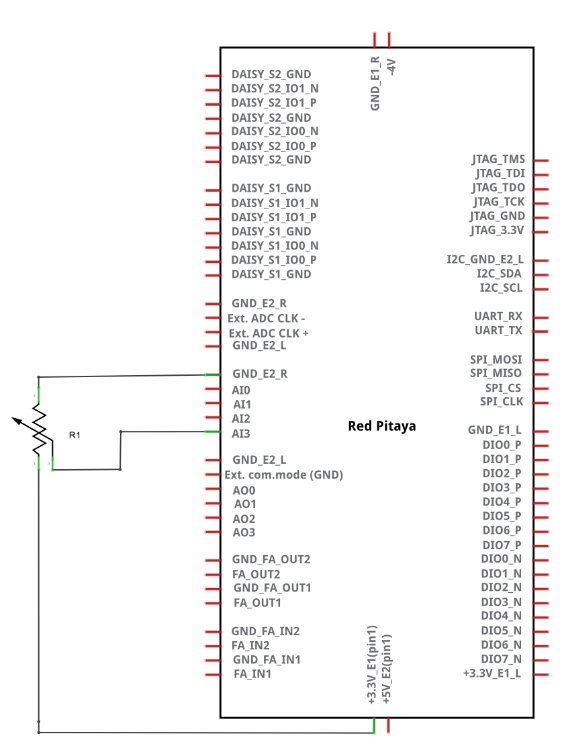
Wiring example for STEMlab 125-14 & STEMlab 125-10:

2.3.6.2.1.3. Circuit
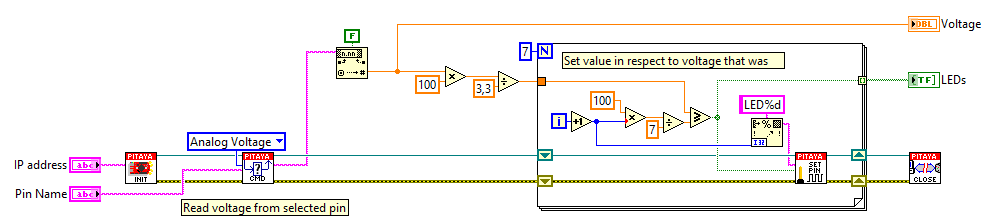
2.3.6.2.1.4. SCPI Code Examples
2.3.6.2.1.4.1. Code - MATLAB®
The code is written in MATLAB. In the code, we use SCPI commands and TCP client communication. Copy the code from below into the MATLAB editor, save the project, and hit the “Run” button.
%% Define Red Pitaya as TCP client object
IP = '192.168.178.108'; % Input IP of your Red Pitaya...
port = 5000;
RP = tcpclient(IP, port);
%% Open connection with your Red Pitaya
RP.ByteOrder = "big-endian";
configureTerminator(RP,"CR/LF");
volts0 = str2double(writeread(RP,'ANALOG:PIN? AIN0'));
volts1 = str2double(writeread(RP,'ANALOG:PIN? AIN1'));
volts2 = str2double(writeread(RP,'ANALOG:PIN? AIN2'));
volts3 = str2double(writeread(RP,'ANALOG:PIN? AIN3'));
%% Close connection with Red Pitaya
clear RP;
2.3.6.2.1.4.2. Code - Python
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import sys
import redpitaya_scpi as scpi
IP = 'rp-f066c8.local'
rp_s = scpi.scpi(IP)
for i in range(4):
rp_s.tx_txt('ANALOG:PIN? AIN' + str(i))
value = float(rp_s.rx_txt())
print ("Measured voltage on AI["+str(i)+"] = "+str(value)+"V")
rp_s.close()
Note
The Python functions are accessible with the latest version of the redpitaya_scpi.py document available on our GitHub. The functions represent a quality-of-life improvement as they combine the SCPI commands in an optimal order and also check for improper user inputs. The code should function at approximately the same speed without them.
For further information on functions please consult the redpitaya_scpi.py code.
2.3.6.2.1.4.3. Code - Scilab
How to set sockets is described in the Blink example.
clc
// Load SOCKET Toolbox
exec(SCI+'contribsocket_toolbox_2.0.1loader.sce');
SOCKET_init();
// Define Red Pitaya as TCP/IP object
IP= '192.168.178.56'; // Input IP of your Red Pitaya...
port = 5000; // If you are using WiFi then IP is:
tcpipObj='RedPitaya'; // 192.168.128.1
// Open connection with your Red Pitaya
SOCKET_open(tcpipObj,IP,port);
// Red value on analog input 3
volts=strtod(SOCKET_query(tcpipObj,'ANALOG:PIN? AIN3'));
disp(volts)
// Define value p from 0 - 100 //
p = volts *(100/3.3) ; // Set value of p in respect to readed voltage
if p >=(100/7)
SOCKET_write(tcpipObj,'DIG:PIN LED1,1')
else
SOCKET_write(tcpipObj,'DIG:PIN LED1,0')
end
if p >=(100/7)*2
SOCKET_write(tcpipObj,'DIG:PIN LED2,1')
else
SOCKET_write(tcpipObj,'DIG:PIN LED2,0')
end
if p >=(100/7)*3
SOCKET_write(tcpipObj,'DIG:PIN LED3,1')
else
SOCKET_write(tcpipObj,'DIG:PIN LED3,0')
end
if p >=(100/7)*4
SOCKET_write(tcpipObj,'DIG:PIN LED4,1')
else
SOCKET_write(tcpipObj,'DIG:PIN LED4,0')
end
if p >=(100/7)*5
SOCKET_write(tcpipObj,'DIG:PIN LED5,1')
else
SOCKET_write(tcpipObj,'DIG:PIN LED5,0')
end
if p >=(100/7)*6
SOCKET_write(tcpipObj,'DIG:PIN LED6,1')
else
SOCKET_write(tcpipObj,'DIG:PIN LED6,0')
end
if p >=(100/7)*7
SOCKET_write(tcpipObj,'DIG:PIN LED7,1')
else
SOCKET_write(tcpipObj,'DIG:PIN LED7,0')
end
// Close connection with Red Pitaya
SOCKET_close(tcpipObj);
2.3.6.2.1.5. API Code Examples
Note
The API code examples don’t require the use of the SCPI server. Instead, the code should be compiled and executed on the Red Pitaya itself (inside Linux OS). Instructions on how to compile the code and other useful information are here.
2.3.6.2.1.5.1. Code - C API
/* Read analog voltage on slow analog input */
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "rp.h"
int main (int argc, char **argv) {
float value [4];
// Initialization of API
if (rp_Init() != RP_OK) {
fprintf(stderr, "Red Pitaya API init failed!\n");
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
// Measure each XADC input voltage
for (int i=0; i<4; i++) {
rp_AIpinGetValue(i, &value[i]);
printf("Measured voltage on AI[%i] = %1.2fV\n", i, value[i]);
}
// Releasing resources
rp_Release();
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
2.3.6.2.1.5.2. Code - Python API
#!/usr/bin/python3
import rp
analog_in = [rp.RP_AIN0, rp.RP_AIN1, rp.RP_AIN2, rp.RP_AIN3]
# Initialize the interface
rp.rp_Init()
# Reset analog pins
rp.rp_ApinReset()
#####! Choose one of two methods, comment the other !#####
#! METHOD 1: Reading all values and selecting the appropriate
#for i in range(4):
# # rp_ApinGetValue returns an array - [0, Input voltage in V, Input voltage RAW]
# value = rp.rp_ApinGetValue(analog_in[i])[1]
# print (f"Measured voltage on AI[{i}] = {value} V")
#! METHOD 2: Read just analog inputs
for i in range(4):
# rp_AIpinGetValue returns an array - [0, Input voltage in V, Input voltage RAW]
value = rp.rp_AIpinGetValue(i)[1]
print (f"Measured voltage on AI[{i}] = {value} V")
# Release resources
rp.rp_Release()