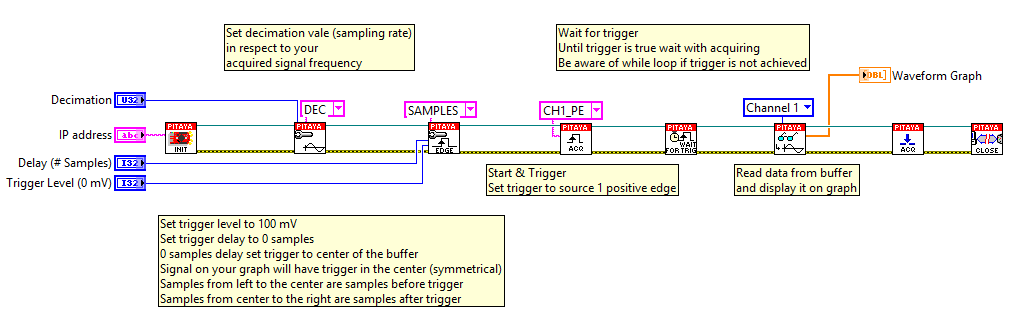
2.3.6.4.1. Triggering with a threshold on channel
2.3.6.4.1.1. Description
This example shows how to acquire 16k samples of a signal on fast analog inputs. The signal will be acquired when the internal trigger condition is met. The time length of the acquired signal depends on the time scale of a buffer that can be set with a decimation factor. The decimations and time scales of a buffer are given in the sample rate and decimation. Voltage and frequency ranges depend on the Red Pitaya model.
2.3.6.4.1.2. Required hardware
Red Pitaya device
Signal (function) generator
Wiring example for STEMlab 125-14 & STEMlab 125-10:
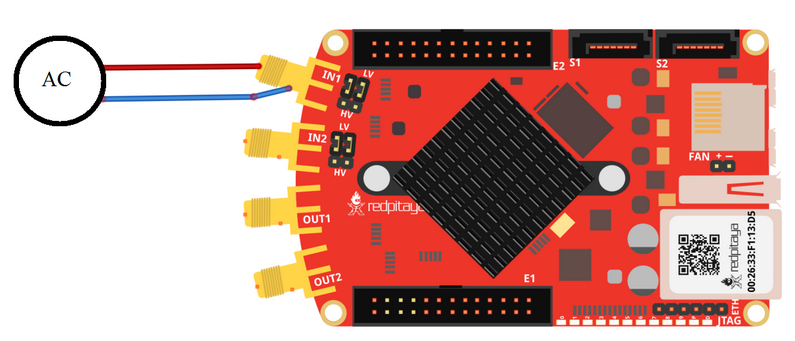
2.3.6.4.1.3. Circuit

2.3.6.4.1.4. SCPI Code Examples
Note
This code is written for 2.00-23 or higher OS. For older OS versions, please check when specific commands were released (a note is added to each command introduced in 2.00 or higher verisons).
Note
With the latest OS versions you can use ACQ:DEC:F <decimation_factor> command for more precise control over the acquisition. The decimation factor can be any of [1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 17, 18, 19, ..., 65535, 65536].
2.3.6.4.1.4.1. Code - MATLAB®
The code is written in MATLAB. In the code, we use SCPI commands and TCP client communication. Copy the code from below into the MATLAB editor, save the project, and hit the “Run” button.
%% Define Red Pitaya as TCP/IP object
clear all
close all
clc
IP = '192.168.178.111'; % Input IP of your Red Pitaya...
port = 5000;
RP = tcpclient(IP, port);
%% Open connection with your Red Pitaya
RP.ByteOrder = 'big-endian';
configureTerminator(RP, 'CR/LF');
flush(RP);
% Reset Acquisition
writeline(RP,'ACQ:RST');
%% ACQUISITION
% Set decimation value (sampling rate) concerning your
% acquired signal frequency
writeline(RP,'ACQ:DEC 1');
writeline(RP,'ACQ:TRig:LEV 0.5'); % trigger level
% SIGNALLAB ONLY
% There is an option to select coupling when using SIGNALlab 250-12
% writeline(RP,'ACQ:SOUR1:COUP AC'); % enables AC coupling on Channel 1
%
% by default LOW level gain is selected
writeline(RP,'ACQ:SOUR1:GAIN LV'); % acquire gain to LV/HV (should the same as jumpers)
% Set trigger delay to 0 samples
% 0 samples delay sets the trigger to the centre of the buffer
% Signal on your graph will have the trigger in the centre (symmetrical)
% Samples from left to centre are samples before the trigger
% Samples from the centre to the right are samples after the trigger
writeline(RP,'ACQ:TRig:DLY 0');
%% Start & Trigg
% Trigger source setting must be after ACQ:START
% Set trigger to source 1 positive edge
writeline(RP,'ACQ:START');
% After acquisition is started some time delay is needed to acquire fresh samples in the buffer
pause(1);
% Here we have used a time delay of one second, but you can calculate the exact value by taking into account the buffer
% length and sampling rate
writeline(RP,'ACQ:TRig CH1_PE');
% Wait for the trigger
% Until the trigger is true wait to acquire
% Be aware of the while loop if the trigger is not achieved
% Ctrl+C will stop code execution in MATLAB
while 1
trig_rsp = writeread(RP,'ACQ:TRig:STAT?')
if strcmp('TD', trig_rsp(1:2)) % Read only TD
break;
end
end
%%! OS 2.00 or higher only !%%
% wait for fill adc buffer
while 1
fill_state = writeread(RP,'ACQ:TRig:FILL?')
if strcmp('1', fill_state(1:1)the )
break;
end
end
%% Read data from the buffer
signal_str = writeread(RP,'ACQ:SOUR1:DATA?');
% Convert values to numbers.
% The first character in the received string is “{“
% and the last 3 are 2 empty spaces and a “}”.
signal_num = str2num(signal_str(1, 2:length(signal_str)-3));
plot(signal_num)
grid on;
ylabel('Voltage / V')
xlabel('Samples')
clear RP;
%% Define Red Pitaya as TCP/IP object
clear all
close all
clc
IP = '192.168.178.111'; % Input IP of your Red Pitaya...
port = 5000;
RP = tcpclient(IP, port);
%% Open connection with your Red Pitaya
RP.ByteOrder = 'big-endian';
configureTerminator(RP, 'CR/LF');
flush(RP);
% Reset Acquisition
writeline(RP,'ACQ:RST');
%% ACQUISITION
writeline(RP,'ACQ:DEC 1');
writeline(RP,'ACQ:TRig:LEV 0.5');
writeline(RP,'ACQ:SOUR1:GAIN LV');
% Set Units and Format
writeline(RP,'ACQ:DATA:FORMAT BIN');
writeline(RP,'ACQ:DATA:Units VOLTS');
% Set trigger delay to 0 samples
% 0 samples delay sets the trigger to the centre of the buffer
% Signal on your graph will have the trigger in the centre (symmetrical)
% Samples from left to centre are samples before the trigger
% Samples from the centre to the right are samples after the trigger
writeline(RP,'ACQ:TRig:DLY 0');
%% Start & Trigg
% Trigger source setting must be after ACQ:START
% Set trigger to source 1 positive edge
writeline(RP,'ACQ:START');
% After acquisition is started some time delay is needed to acquire fresh samples in the buffer
pause(1);
% Here we have used a time delay of one second, but you can calculate the exact value by taking into account the buffer
% length and sampling rate
writeline(RP,'ACQ:TRig CH1_PE');
% Wait for the trigger
% Until the trigger is true wait to acquire
% Be aware of the while loop if the trigger is not achieved
% Ctrl+C will stop code execution in MATLAB
while 1
trig_rsp = writeread(RP,'ACQ:TRig:STAT?')
if strcmp('TD', trig_rsp(1:2)) % Read only TD
break
end
end
%%! OS 2.00 or higher only !%%
% wait for fill adc buffer
while 1
fill_state = writeread(RP,'ACQ:TRig:FILL?')
if strcmp('1', fill_state(1:1))
break;
end
end
% Read data from the buffer
writeline(RP,'ACQ:SOUR1:DATA?');
% Read header for binary format
header = read(RP, 1);
% Reading size of the block, what informed about data size
header_size = str2double(strcat(read(RP, 1, 'int8')));
% Reading size of data
data_size = str2double(strcat(read(RP, header_size, 'char'))');
% Read data
signal_num = read(RP, data_size/4,'float');
plot(signal_num)
grid on
ylabel('Voltage / V')
xlabel('samples')
clear RP;
%% Define Red Pitaya as TCP/IP object
clear all
close all
clc
IP = '192.168.178.111'; % Input IP of your Red Pitaya...
port = 5000;
RP = tcpclient(IP, port);
%% Open connection with your Red Pitaya
RP.ByteOrder = 'big-endian';
configureTerminator(RP, 'CR/LF');
flush(RP);
% Set decimation vale (sampling rate) concerning you
% acquired signal frequency
% Reset Acquisition
writeline(RP,'ACQ:RST');
%% ACQUISITION
writeline(RP,'ACQ:DEC 1');
writeline(RP,'ACQ:TRig:LEV 0.5');
writeline(RP,'ACQ:SOUR1:GAIN LV');
% Select Format and Units
writeline(RP,'ACQ:DATA:FORMAT BIN');
writeline(RP,'ACQ:DATA:Units RAW');
% Set trigger delay to 0 samples
% 0 samples delay the et trigger to the centre of the buffer
% Signal on your graph will have a trigger in the centre (symmetrical)
% Samples from left to centre are samples before the trigger
% Samples from the centre to the right are samples after the trigger
writeline(RP,'ACQ:TRig:DLY 0');
%% Start & Trigg
% Trigger source setting must be after ACQ:START
% Set trigger to source 1 positive edge
writeline(RP,'ACQ:START');
% After the acquisition is started some time delay is needed to acquire fresh samples in to buffer
% Here we have used a time delay of one second but you can calculate the exact value taking into account the buffer
% length and sampling rate
pause(1);
writeline(RP,'ACQ:TRig CH1_PE');
% Wait for the trigger
% Until the trigger is true wait to acquire
% Be aware of the while loop if the trigger is not achieved
% Ctrl+C will stop code executing in MATLAB
while 1
trig_rsp = writeread(RP,'ACQ:TRig:STAT?')
if strcmp('TD',trig_rsp(1:2)) % Read only TD
break;
end
end
%%! OS 2.00 or higher only !%%
% wait for fill adc buffer
while 1
fill_state = writeread(RP,'ACQ:TRig:FILL?')
if strcmp('1', fill_state(1:1))
break;
end
end
% Read data from the buffer
writeline(RP,'ACQ:SOUR1:DATA?');
% Read header for binary format
header = read(RP, 1);
% Reading size of the block, what informed about data size
header_size = str2double(strcat(read(RP, 1, 'int8')));
% Reading size of data
data_size = str2double(strcat(read(RP, header_size, 'char'))');
% Read data
signal_num = read(RP, data_size/2, 'int16');
plot(signal_num)
grid on;
ylabel('Voltage / V')
xlabel('samples')
clear RP;
%% Define Red Pitaya as TCP/IP object
clear all
close all
clc
IP = '192.168.178.111'; % Input IP of your Red Pitaya...
port = 5000;
RP = tcpclient(IP, port);
%% Open connection with your Red Pitaya
RP.ByteOrder = "big-endian";
configureTerminator(RP,"CR/LF");
flush(RP);
% Reset Acquisition
writeline(RP,'ACQ:RST');
%% ACQUISITION
writeline(RP,'ACQ:DEC 1');
writeline(RP,'ACQ:TRig:LEV 0.5');
% Set trigger delay to 0 samples
% 0 samples delay set the trigger to the centre of the buffer
% Signal on your graph will have a trigger in the centre (symmetrical)
% Samples from left to centre are samples before the trigger
% Samples from the centre to the right are samples after the trigger
writeline(RP,'ACQ:TRig:DLY 0');
%% Start & Trigg
% Trigger source setting must be after ACQ:START
% Set trigger to source 1 positive edge
writeline(RP,'ACQ:START');
% After the acquisition is started some time delay is needed to acquire fresh samples in to buffer
% Here we have used a time delay of one second but you can calculate the exact value taking into account the buffer
% length and sampling rate
pause(1);
writeline(RP,'ACQ:TRig CH1_PE');
% Wait for the trigger
% Until the trigger is true wait to acquire
% Be aware of the while loop if the trigger is not achieved
% Ctrl+C will stop code executing in Matlab
while 1
trig_rsp = writeread(RP,'ACQ:TRig:STAT?')
if strcmp('TD', trig_rsp(1:2)) % Read only TD
break;
end
end
%%! OS 2.00 or higher only !%%
% wait for fill adc buffer
while 1
fill_state = writeread(RP,'ACQ:TRig:FILL?')
if strcmp('1', fill_state(1:1))
break;
end
end
% Read data from the buffer
signal_str = writeread(RP,'ACQ:SOUR1:DATA?');
signal_str_2 = writeread(RP,'ACQ:SOUR2:DATA?');
signal_str_3 = writeread(RP,'ACQ:SOUR3:DATA?');
signal_str_4 = writeread(RP,'ACQ:SOUR4:DATA?');
% Convert values to numbers.% First character in the string is “{“
% and 2 latest are empty spaces and the last is “}”.
signal_num = str2num(signal_str(1,2:length(signal_str)-3));
signal_num_2 = str2num(signal_str_2(1,2:length(signal_str_2)-3));
signal_num_3 = str2num(signal_str_3(1,2:length(signal_str_3)-3));
signal_num_4 = str2num(signal_str_4(1,2:length(signal_str_4)-3));
plot(signal_num,'r')
hold on
plot(signal_num_2,'g')
hold on
plot(signal_num_3,'b')
hold on
plot(signal_num_4,'m')
grid on
ylabel('Voltage / V')
xlabel('samples')
clear RP;
2.3.6.4.1.4.2. Code - Python
Using just SCPI commands:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import sys
import redpitaya_scpi as scpi
import matplotlib.pyplot as plot
IP = 'rp-f066c8.local'
rp_s = scpi.scpi(IP)
rp_s.tx_txt('ACQ:RST')
rp_s.tx_txt('ACQ:DATA:FORMAT ASCII')
rp_s.tx_txt('ACQ:DATA:Units VOLTS')
rp_s.tx_txt('ACQ:DEC 1')
rp_s.tx_txt('ACQ:TRig:LEV 0.5')
rp_s.tx_txt('ACQ:START')
rp_s.tx_txt('ACQ:TRig CH1_PE')
while 1:
rp_s.tx_txt('ACQ:TRig:STAT?')
if rp_s.rx_txt() == 'TD':
break
## ! OS 2.00 or higher only ! ##
while 1:
rp_s.tx_txt('ACQ:TRig:FILL?')
if rp_s.rx_txt() == '1':
break
rp_s.tx_txt('ACQ:SOUR1:DATA?')
buff_string = rp_s.rx_txt()
buff_string = buff_string.strip('{}\n\r').replace(" ", "").split(',')
buff = list(map(float, buff_string))
plot.plot(buff)
plot.ylabel('Voltage')
plot.show()
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import sys
import redpitaya_scpi as scpi
import matplotlib.pyplot as plot
import struct
IP = 'rp-f066c8.local'
rp_s = scpi.scpi(IP)
rp_s.tx_txt('ACQ:RST')
rp_s.tx_txt('ACQ:DATA:FORMAT BIN')
rp_s.tx_txt('ACQ:DATA:Units VOLTS')
rp_s.tx_txt('ACQ:DEC 1')
rp_s.tx_txt('ACQ:TRig:LEV 0.5')
rp_s.tx_txt('ACQ:START')
rp_s.tx_txt('ACQ:TRig CH1_PE')
while 1:
rp_s.tx_txt('ACQ:TRig:STAT?')
if rp_s.rx_txt() == 'TD':
break
## ! OS 2.00 or higher only ! ##
while 1:
rp_s.tx_txt('ACQ:TRig:FILL?')
if rp_s.rx_txt() == '1':
break
rp_s.tx_txt('ACQ:SOUR1:DATA?')
buff_byte = rp_s.rx_arb()
buff = [struct.unpack('!f',bytearray(buff_byte[i:i+4]))[0] for i in range(0, len(buff_byte), 4)]
plot.plot(buff)
plot.ylabel('Voltage')
plot.show()
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import sys
import redpitaya_scpi as scpi
import matplotlib.pyplot as plot
import struct
IP = 'rp-f066c8.local'
rp_s = scpi.scpi(IP)
rp_s.tx_txt('ACQ:RST')
rp_s.tx_txt('ACQ:DATA:FORMAT BIN')
rp_s.tx_txt('ACQ:DATA:Units RAW')
rp_s.tx_txt('ACQ:DEC 1')
rp_s.tx_txt('ACQ:TRig:LEV 0.5')
rp_s.tx_txt('ACQ:START')
rp_s.tx_txt('ACQ:TRig CH1_PE')
while 1:
rp_s.tx_txt('ACQ:TRig:STAT?')
if rp_s.rx_txt() == 'TD':
break
## ! OS 2.00 or higher only ! ##
while 1:
rp_s.tx_txt('ACQ:TRig:FILL?')
if rp_s.rx_txt() == '1':
break
rp_s.tx_txt('ACQ:SOUR1:DATA?')
buff_byte = rp_s.rx_arb()
buff = [struct.unpack('!h',bytearray(buff_byte[i:i+2]))[0] for i in range(0, len(buff_byte), 2)]
plot.plot(buff)
plot.ylabel('Voltage')
plot.show()
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import sys
import redpitaya_scpi as scpi
import matplotlib.pyplot as plot
IP = 'rp-f066c8.local'
rp_s = scpi.scpi(IP)
rp_s.tx_txt('ACQ:RST')
rp_s.tx_txt('ACQ:DATA:FORMAT ASCII')
rp_s.tx_txt('ACQ:DATA:Units VOLTS')
rp_s.tx_txt('ACQ:DEC 1')
rp_s.tx_txt('ACQ:TRig:LEV 0.5')
rp_s.tx_txt('ACQ:TRig:DLY 0')
rp_s.tx_txt('ACQ:START')
rp_s.tx_txt('ACQ:TRig CH1_PE')
while 1:
rp_s.tx_txt('ACQ:TRig:STAT?')
if rp_s.rx_txt() == 'TD':
break
## ! OS 2.00 or higher only ! ##
while 1:
rp_s.tx_txt('ACQ:TRig:FILL?')
if rp_s.rx_txt() == '1':
break
rp_s.tx_txt('ACQ:SOUR1:DATA?')
buff_string = rp_s.rx_txt()
buff_string = buff_string.strip('{}\n\r').replace(" ", "").split(',')
buff = list(map(float, buff_string))
rp_s.tx_txt('ACQ:SOUR2:DATA?')
buff_string = rp_s.rx_txt()
buff_string = buff_string.strip('{}\n\r').replace(" ", "").split(',')
buff2 = list(map(float, buff_string))
rp_s.tx_txt('ACQ:SOUR3:DATA?')
buff_string = rp_s.rx_txt()
buff_string = buff_string.strip('{}\n\r').replace(" ", "").split(',')
buff3 = list(map(float, buff_string))
rp_s.tx_txt('ACQ:SOUR4:DATA?')
buff_string = rp_s.rx_txt()
buff_string = buff_string.strip('{}\n\r').replace(" ", "").split(',')
buff4 = list(map(float, buff_string))
plot.plot(buff, 'r')
plot.plot(buff2, 'g')
plot.plot(buff3, 'b')
plot.plot(buff4, 'm')
plot.ylabel('Voltage')
plot.show()
Using functions:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import sys
import redpitaya_scpi as scpi
import matplotlib.pyplot as plot
IP = 'rp-f066c8.local'
rp_s = scpi.scpi(IP)
rp_s.tx_txt('ACQ:RST')
dec = 1
trig_lvl = 0.5
# Function for configuring Acquisition
rp_s.acq_set(dec, trig_lvl, units='volts', form='ascii')
rp_s.tx_txt('ACQ:START')
rp_s.tx_txt('ACQ:TRig CH1_PE')
while 1:
rp_s.tx_txt('ACQ:TRig:STAT?')
if rp_s.rx_txt() == 'TD':
break
## ! OS 2.00 or higher only ! ##
while 1:
rp_s.tx_txt('ACQ:TRig:FILL?')
if rp_s.rx_txt() == '1':
break
# function for Data Acquisition
buff = rp_s.acq_data(1, bin= False, convert= True)
plot.plot(buff)
plot.ylabel('Voltage')
plot.show()
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import sys
import redpitaya_scpi as scpi
import matplotlib.pyplot as plot
import struct
IP = 'rp-f066c8.local'
rp_s = scpi.scpi(IP)
rp_s.tx_txt('ACQ:RST')
dec = 1
trig_lvl = 0.5
# Function for configuring Acquisition
rp_s.acq_set(dec, trig_lvl, units='volts', form='bin')
rp_s.tx_txt('ACQ:START')
rp_s.tx_txt('ACQ:TRig CH1_PE')
while 1:
rp_s.tx_txt('ACQ:TRig:STAT?')
if rp_s.rx_txt() == 'TD':
break
## ! OS 2.00 or higher only ! ##
while 1:
rp_s.tx_txt('ACQ:TRig:FILL?')
if rp_s.rx_txt() == '1':
break
# function for Data Acquisition
buff = rp_s.acq_data(1, bin= True, convert= True)
plot.plot(buff)
plot.ylabel('Voltage')
plot.show()
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import sys
import redpitaya_scpi as scpi
import matplotlib.pyplot as plot
import struct
IP = 'rp-f066c8.local'
rp_s = scpi.scpi(IP)
rp_s.tx_txt('ACQ:RST')
dec = 1
trig_lvl = 0.5
# Function for configuring Acquisition
rp_s.acq_set(dec, trig_lvl, units='raw', form='bin')
rp_s.tx_txt('ACQ:START')
rp_s.tx_txt('ACQ:TRig CH1_PE')
while 1:
rp_s.tx_txt('ACQ:TRig:STAT?')
if rp_s.rx_txt() == 'TD':
break
## ! OS 2.00 or higher only ! ##
while 1:
rp_s.tx_txt('ACQ:TRig:FILL?')
if rp_s.rx_txt() == '1':
break
# function for Data Acquisition
buff = rp_s.acq_data(1, bin= True, convert= True)
plot.plot(buff)
plot.ylabel('Voltage')
plot.show()
#!/usr/bin/python3
import sys
import redpitaya_scpi as scpi
import matplotlib.pyplot as plot
IP = 'rp-f066c8.local'
rp_s = scpi.scpi(IP)
rp_s.tx_txt('ACQ:RST')
dec = 1
trig_lvl = 0.5
trig_delay = 0
# Function for configuring Acquisition
rp_s.acq_set(dec, trig_lvl, trig_delay, units='volts', form='ascii', input4=True)
rp_s.tx_txt('ACQ:START')
rp_s.tx_txt('ACQ:TRig CH1_PE')
while 1:
rp_s.tx_txt('ACQ:TRig:STAT?')
if rp_s.rx_txt() == 'TD':
break
## ! OS 2.00 or higher only ! ##
while 1:
rp_s.tx_txt('ACQ:TRig:FILL?')
if rp_s.rx_txt() == '1':
break
# function for Data Acquisition
buff = rp_s.acq_data(1, bin= False, convert= True, input4 =True)
buff2 = rp_s.acq_data(2, bin= False, convert= True, input4 =True)
buff3 = rp_s.acq_data(3, bin= False, convert= True, input4 =True)
buff4 = rp_s.acq_data(4, bin= False, convert= True, input4 =True)
plot.plot(buff, 'r')
plot.plot(buff2, 'g')
plot.plot(buff3, 'b')
plot.plot(buff4, 'm')
plot.ylabel('Voltage')
plot.show()
Note
The Python functions are accessible with the latest version of the redpitaya_scpi.py document available on our GitHub. The functions represent a quality-of-life improvement as they combine the SCPI commands in an optimal order and also check for improper user inputs. The code should function at approximately the same speed without them.
For further information on functions please consult the redpitaya_scpi.py code.
2.3.6.4.1.4.3. Code - Scilab
Scilab socket input buffer can read approximately 800 samples from Red Pitaya. This is the problem in contributed code for Scilab sockets. How to set the socket is described in the Blink example.
clear all
clc
// Load SOCKET Toolbox.
exec(SCI+'contribsocket_toolbox_2.0.1loader.sce');
SOCKET_init();
// Define Red Pitaya as TCP/IP object
IP= '192.168.178.56'; // Input IP of your Red Pitaya...
port = 5000; // If you are using WiFi then IP is:
tcpipObj='RedPitaya'; // 192.168.128.1
// Open connection with your Red Pitaya
SOCKET_open(tcpipObj,IP,port);
// Set decimation value (sampling rate) concerning you
// acquired signal frequency
SOCKET_write(tcpipObj,'ACQ:RST');
SOCKET_write(tcpipObj,'ACQ:DEC 8');
// Set trigger level to 500 mV
SOCKET_write(tcpipObj,'ACQ:TRig:LEV 0.5');
//There is an option to select coupling when using SIGNALlab 250-12
// SOCKET_write(tcpipObj,'ACQ:SOUR1:COUP AC'); // enables AC coupling on Channel 1
//By default LOW-level gain is selected
SOCKET_write(tcpipObj,'ACQ:SOUR1:GAIN LV'); // user can switch gain using this command
// Set trigger delay to 0 samples
// 0 samples delay set trigger to centre of the buffer
// Signal on your graph will have a trigger in the centre (symmetrical)
// Samples from left to centre are samples before the trigger
// Samples from the centre to the right are samples after the trigger
SOCKET_write(tcpipObj,'ACQ:TRig:DLY 0');
//// Start & Trigg
// Trigger source setting must be after ACQ:START
// Set trigger to source 1 positive edge
SOCKET_write(tcpipObj,'ACQ:START');
SOCKET_write(tcpipObj,'ACQ:TRig CH1_PE');
// Wait for the trigger
// Until the trigger is true wait to acquire
// Be aware of the while loop if the trigger is not achieved
// Ctrl+C will stop code executing
xpause(1E+6)
// Read data from the buffer
signal_str=SOCKET_query(tcpipObj,'ACQ:SOUR1:DATA:OLD:N? 800');
// Convert values to numbers.// First character in the string is “{“
// and 2 latest are empty spaces and the last is “}”.
signal_str=part(signal_str, 2:length(signal_str)-3)
signal_num=strtod(strsplit(signal_str,",",length(signal_str)))';
plot(signal_num)
SOCKET_close(tcpipObj);
2.3.6.4.1.5. API Code Examples
Note
The API code examples don’t require the use of the SCPI server. Instead, the code should be compiled and executed on the Red Pitaya itself (inside Linux OS). Instructions on how to compile the code and other useful information are here.
2.3.6.4.1.5.1. Code - C API
/* Red Pitaya C API example of Acquiring a signal on external trigger on a specific channel */
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include "rp.h"
int main(int argc, char **argv){
/* Print error, if rp_Init() function failed */
if(rp_Init() != RP_OK){
fprintf(stderr, "Rp api init failed!\n");
}
/* Reset Generation and Acquisition */
rp_GenReset();
rp_AcqReset();
/* Generation */
/*LOOB BACK FROM OUTPUT 2 - ONLY FOR TESTING*/
rp_GenFreq(RP_CH_1, 20000.0);
rp_GenAmp(RP_CH_1, 1.0);
rp_GenWaveform(RP_CH_1, RP_WAVEFORM_SINE);
rp_GenOutEnable(RP_CH_1);
/* Acquisition */
uint32_t buff_size = 16384;
float *buff = (float *)malloc(buff_size * sizeof(float));
rp_AcqSetDecimation(RP_DEC_8);
rp_AcqSetTriggerLevel(RP_CH_1, 0.5); // Trig level is set in Volts while in SCPI
rp_AcqSetTriggerDelay(0);
// There is an option to select coupling when using SIGNALlab 250-12
// rp_AcqSetAC_DC(RP_CH_1, RP_AC); // enables AC coupling on Channel 1
// By default LV level gain is selected
rp_AcqSetGain(RP_CH_1, RP_LOW); // user can switch gain using this command
rp_AcqStart();
/* After the acquisition is started some time delay is needed to acquire fresh samples into buffer
Here we have used a time delay of one second but you can calculate the exact value taking into account buffer
length and sampling rate */
sleep(1);
rp_AcqSetTriggerSrc(RP_TRIG_SRC_CHA_PE);
rp_acq_trig_state_t state = RP_TRIG_STATE_TRIGGERED;
while(1){
rp_AcqGetTriggerState(&state);
if(state == RP_TRIG_STATE_TRIGGERED){
break;
}
}
// !! OS 2.00 or higher only !! //
bool fillState = false;
while(!fillState){
rp_AcqGetBufferFillState(&fillState);
}
rp_AcqGetOldestDataV(RP_CH_1, &buff_size, buff);
int i;
for(i = 0; i < buff_size; i++){
printf("%f\n", buff[i]);
}
/* Releasing resources */
free(buff);
rp_Release();
return 0;
}
/* Red Pitaya C API example of Acquiring a signal on external trigger on a specific channel */
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include "rp.h"
int main(int argc, char **argv){
/* Print error, if rp_Init() function failed */
if(rp_Init() != RP_OK){
fprintf(stderr, "Rp api init failed!\n");
}
uint32_t buff_size = 16384;
float *buff_ch1 = (float *)malloc(buff_size * sizeof(float));
float *buff_ch2 = (float *)malloc(buff_size * sizeof(float));
float *buff_ch3 = (float *)malloc(buff_size * sizeof(float));
float *buff_ch4 = (float *)malloc(buff_size * sizeof(float));
/* Reset Acquisition */
rp_AcqReset();
/* Acquisition */
rp_AcqSetDecimation(RP_DEC_8);
rp_AcqSetTriggerLevel(RP_CH_1, 0.5);
rp_AcqSetTriggerDelay(0);
rp_AcqStart();
/* After the acquisition is started some time delay is needed to acquire fresh samples into buffer
Here we have used a time delay of one second but you can calculate the exact value taking into account buffer
length and sampling rate*/
sleep(1);
rp_AcqSetTriggerSrc(RP_TRIG_SRC_CHA_PE);
rp_acq_trig_state_t state = RP_TRIG_STATE_TRIGGERED;
while(1){
rp_AcqGetTriggerState(&state);
if(state == RP_TRIG_STATE_TRIGGERED){
sleep(1);
break;
}
}
// !! OS 2.00 or higher only !! //
bool fillState = false;
while(!fillState){
rp_AcqGetBufferFillState(&fillState);
}
uint32_t pos = 0;
rp_AcqGetWritePointerAtTrig(&pos);
rp_AcqGetDataV2(pos, &buff_size, buff_ch1,buff_ch2, buff_ch3, buff_ch4);
int i;
for(i = 0; i < buff_size; i++){
printf("%f %f %f %f\n", buff_ch1[i],buff_ch2[i],buff_ch3[i],buff_ch4[i]);
}
/* Releasing resources */
free(buff_ch1);
free(buff_ch2);
free(buff_ch3);
free(buff_ch4);
rp_Release();
return 0;
}
2.3.6.4.1.5.2. Code - Python API
#!/usr/bin/python3
import time
import numpy as np
import rp
#? Possible waveforms:
#? RP_WAVEFORM_SINE, RP_WAVEFORM_SQUARE, RP_WAVEFORM_TRIANGLE, RP_WAVEFORM_RAMP_UP,
#? RP_WAVEFORM_RAMP_DOWN, RP_WAVEFORM_DC, RP_WAVEFORM_PWM, RP_WAVEFORM_ARBITRARY,
#? RP_WAVEFORM_DC_NEG, RP_WAVEFORM_SWEEP
channel = rp.RP_CH_1
channel2 = rp.RP_CH_2
waveform = rp.RP_WAVEFORM_SINE
freq = 100000
ampl = 1.0
#? Possible decimations:
#? RP_DEC_1, RP_DEC_2, RP_DEC_4, RP_DEC_8, RP_DEC_16 , RP_DEC_32 , RP_DEC_64 ,
#? RP_DEC_128, RP_DEC_256, RP_DEC_512, RP_DEC_1024, RP_DEC_2048, RP_DEC_4096, RP_DEC_8192,
#? RP_DEC_16384, RP_DEC_32768, RP_DEC_65536
dec = rp.RP_DEC_1
trig_lvl = 0.5
trig_dly = 0
#? Possible acquisition trigger sources:
#? RP_TRIG_SRC_DISABLED, RP_TRIG_SRC_NOW, RP_TRIG_SRC_CHA_PE, RP_TRIG_SRC_CHA_NE, RP_TRIG_SRC_CHB_PE,
#? RP_TRIG_SRC_CHB_NE, RP_TRIG_SRC_EXT_PE, RP_TRIG_SRC_EXT_NE, RP_TRIG_SRC_AWG_PE, RP_TRIG_SRC_AWG_NE,
#? RP_TRIG_SRC_CHC_PE, RP_TRIG_SRC_CHC_NE, RP_TRIG_SRC_CHD_PE, RP_TRIG_SRC_CHD_NE
acq_trig_sour = rp.RP_TRIG_SRC_CHA_PE
N = 16384
# Initialize the interface
rp.rp_Init()
# Reset Generation and Acquisition
rp.rp_GenReset()
rp.rp_AcqReset()
###### Generation #####
# OUT1
print("Gen_start")
rp.rp_GenWaveform(channel, waveform)
rp.rp_GenFreqDirect(channel, freq)
rp.rp_GenAmp(channel, ampl)
# OUT2
rp.rp_GenWaveform(channel2, waveform)
rp.rp_GenFreqDirect(channel2, freq)
rp.rp_GenAmp(channel2, ampl)
#? Possible trigger sources:
#? RP_GEN_TRIG_SRC_INTERNAL, RP_GEN_TRIG_SRC_EXT_PE, RP_GEN_TRIG_SRC_EXT_NE
# Specify generator trigger source
rp.rp_GenTriggerSource(channel, rp.RP_GEN_TRIG_SRC_INTERNAL)
# Enable output synchronisation
rp.rp_GenOutEnableSync(True)
##### Acquisition #####
# Set Decimation
rp.rp_AcqSetDecimation(rp.RP_DEC_1)
#? Possible triggers:
#? RP_T_CH_1, RP_T_CH_2, RP_T_CH_EXT
# Set trigger level and delay
rp.rp_AcqSetTriggerLevel(rp.RP_T_CH_1, trig_lvl)
rp.rp_AcqSetTriggerDelay(trig_dly)
# Start Acquisition
print("Acq_start")
rp.rp_AcqStart()
# Specify trigger - input 1 positive edge
rp.rp_AcqSetTriggerSrc(acq_trig_sour)
rp.rp_GenTriggerOnly(channel) # Trigger generator
# Trigger state
while 1:
trig_state = rp.rp_AcqGetTriggerState()[1]
if trig_state == rp.RP_TRIG_STATE_TRIGGERED:
break
## ! OS 2.00 or higher only ! ##
# Fill state
while 1:
if rp.rp_AcqGetBufferFillState()[1]:
break
# Get data
# RAW
ibuff = rp.i16Buffer(N)
res = rp.rp_AcqGetOldestDataRaw(rp.RP_CH_1, N, ibuff.cast())
# Volts
fbuff = rp.fBuffer(N)
res = rp.rp_AcqGetDataV(rp.RP_CH_1, 0, N, fbuff)
data_V = np.zeros(N, dtype = float)
data_raw = np.zeros(N, dtype = int)
for i in range(0, N, 1):
data_V[i] = fbuff[i]
data_raw[i] = ibuff[i]
print(f"Data in Volts: {data_V}")
print(f"Raw data: {data_raw}")
# Release resources
rp.rp_Release()
#!/usr/bin/python3
import time
import numpy as np
import rp
#? Possible channels
#? RP_CH_1, RP_CH_2, RP_CH_3, RP_CH_4
acq_channel = rp.RP_CH_1
#? Possible decimations:
#? RP_DEC_1, RP_DEC_2, RP_DEC_4, RP_DEC_8, RP_DEC_16 , RP_DEC_32 , RP_DEC_64 ,
#? RP_DEC_128, RP_DEC_256, RP_DEC_512, RP_DEC_1024, RP_DEC_2048, RP_DEC_4096, RP_DEC_8192,
#? RP_DEC_16384, RP_DEC_32768, RP_DEC_65536
dec = rp.RP_DEC_1
trig_lvl = 0.5
trig_dly = 0
#? Possible acquisition trigger sources:
#? RP_TRIG_SRC_DISABLED, RP_TRIG_SRC_NOW, RP_TRIG_SRC_CHA_PE, RP_TRIG_SRC_CHA_NE, RP_TRIG_SRC_CHB_PE,
#? RP_TRIG_SRC_CHB_NE, RP_TRIG_SRC_EXT_PE, RP_TRIG_SRC_EXT_NE, RP_TRIG_SRC_AWG_PE, RP_TRIG_SRC_AWG_NE,
#? RP_TRIG_SRC_CHC_PE, RP_TRIG_SRC_CHC_NE, RP_TRIG_SRC_CHD_PE, RP_TRIG_SRC_CHD_NE
acq_trig_sour = rp.RP_TRIG_SRC_CHA_PE
N = 16384
# Initialize the interface
rp.rp_Init()
# Reset Acquisition
rp.rp_AcqReset()
##### Acquisition #####
# Set Decimation
rp.rp_AcqSetDecimation(rp.RP_DEC_1)
#? Possible triggers:
#? RP_T_CH_1, RP_T_CH_2, RP_T_CH_3, RP_T_CH_4, RP_T_CH_EXT
# Set trigger level and delay
rp.rp_AcqSetTriggerLevel(rp.RP_T_CH_1, trig_lvl)
rp.rp_AcqSetTriggerDelay(trig_dly)
# Start Acquisition
print("Acq_start")
rp.rp_AcqStart()
# Specify trigger - input 1 positive edge
rp.rp_AcqSetTriggerSrc(acq_trig_sour)
# Trigger state
while 1:
trig_state = rp.rp_AcqGetTriggerState()[1]
if trig_state == rp.RP_TRIG_STATE_TRIGGERED:
break
## ! OS 2.00 or higher only ! ##
# Fill state
while 1:
if rp.rp_AcqGetBufferFillState()[1]:
break
# Get data
# RAW
ibuff = rp.i16Buffer(N)
res = rp.rp_AcqGetOldestDataRaw(acq_channel, N, ibuff.cast())
# Volts
fbuff = rp.fBuffer(N)
res = rp.rp_AcqGetDataV(acq_channel, 0, N, fbuff)
data_V = np.zeros(N, dtype = float)
data_raw = np.zeros(N, dtype = int)
for i in range(0, N, 1):
data_V[i] = fbuff[i]
data_raw[i] = ibuff[i]
print(f"Data in Volts: {data_V}")
print(f"Raw data: {data_raw}")
# Release resources
rp.rp_Release()